When the Hamiltonian is independent of time, the state function can be written as a product of a function of time and a function of position. ![]()
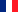
Substituting into the time-dependent Schrödinger equation: 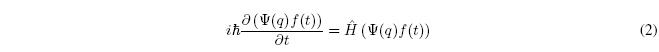
Since \(\Psi\) does not depend on t and \(\hat{H}\) does not depend on either, we can take \(\Psi (q)\) from the time derivative and \(f(t)\) from the Hamiltonian. ![]()
Dividing the terms of equation (3) by \(f(t)\Psi (q)\) gives us: 
The member on the left depends only on t and the one on the right only on the coordinates q. Thus, equality is only possible if both terms are equal to a constant that we will call E. 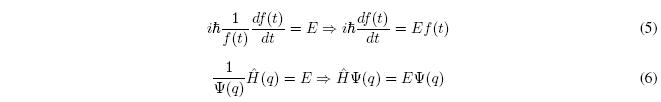
The first equation gives us the temporal evolution of the system (temporal Schrödinger equation). The second equation is the spatial or time-independent Schödinger equation.
We integrate the temporal Schrödinger equation: 
where C is the constant of integration. Taking antilogarithms, the function f(t) is obtained. ![]()
The constant A can be included in the function \(\Psi (q)\) as a multiplicative factor, thus, we can write the above equation as: ![]()
Therefore, in those systems in which the Hamiltonian does not depend on t, the state function can be written: ![]()
The states of a physical system that can be written in the above way are characterized by having a constant energy and are called stationary states. Stationary states are characterized by having a probability density independent of time. ![]()
Therefore, for a system with \(\hat{H}\) independent of t, the total energy is constant and the probability that the particle has its coordinates between \(q\) and \(q+dq\) is not it changes over time.