The chemical compounds
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1239
Chemical elements are formed by a single type of atom (Na, K, O 2 , N 2 ), while compounds are formed by the union of two or more types of atoms. Water is a chemical compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen (H 2 O). Carbon dioxide is made up of one carbon atom and two oxygen (CO 2 ). Chemical compounds are represented by the symbols of the elements that form them accompanied by subscripts that indicate the proportion in which these elements participate.
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1463
 The bonds that unite the different atoms that form a chemical compound can be ionic or covalent. In covalent bonds, electrons are shared, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms. Ionic bonds usually form between metals and non-metals (NaCl). Covalent bonds are frequent between non-metallic elements.
The bonds that unite the different atoms that form a chemical compound can be ionic or covalent. In covalent bonds, electrons are shared, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms. Ionic bonds usually form between metals and non-metals (NaCl). Covalent bonds are frequent between non-metallic elements.
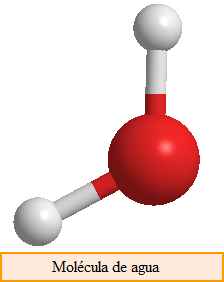
Molecular compounds, are formed by molecules, consisting of atoms joined by covalent bond. Molecules are represented by a chemical formula that indicates the types of atoms present and the proportion in which they participate.
H 2 O: molecule formed by hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 2 to 1.
CCl 4 : molecule formed by carbon and hydrogen in a ratio of 1 to 4
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1364
The empirical formula indicates the atoms that participate in the compound as well as their proportion. For example, glucose has the empirical formula CH 2 O, which indicates the presence of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen in its structure in a 1:2:1 ratio. However, the actual formula of the glucose molecule is C 6 H 12 O 6.
Molecular formula , it is the real formula of the molecule, it indicates the types of atoms and the number of each type that participate in the formation of the molecule. For example, the molecular formula for glucose, C 6 H 12 O 6 , tells us that each molecule is made up of 6 C atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms.
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1243
The mass of a molecule is obtained by adding the masses of the atoms that compose it. Let's see an example:
Calculate the molecular mass of water knowing that the atomic masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 1,008 and 15,999 amu.
The water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen, its mass will be given by the sum of two times the mass of hydrogen plus the mass of oxygen.
m(H 2 O) = 2m(H 2 )+ m(O 2 ) = 2x1,008 + 15,999 = 18,015 amu
A mole of a substance represents the quantity in grams equal to the molecular weight and contains 6.02214x10 23 molecules.
The molecular mass of water is 18.015 amu, therefore, a mole of water is 18.015 g and contains 6.02214x10 23 water molecules.
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1357
Let's calculate the percent composition of acetic acid: C 2 H 4 O 2
- Determining the mass of a mole of substance
m(C 2 H 4 O 2 ) = 12.01, x 2 + 1.008 x 4 + 15.99 x 2 = 60.04 g/mol
- Calculation of the percentage of each element in the compound, dividing the mass of the element by the mass of one mole of the compound
$$\%C=\frac{12.01 \cdot 2}{60.04}\cdot 100 =40.00\%$$
$$\%H=\frac{1.008 \cdot 4}{60.04}\cdot 100 =6.728\%$$
$$\%O=\frac{15.99 \cdot 2}{60.04}\cdot 100 =53.26\%$$
The experimental determination of the percent composition of a compound and its comparison with the theoretical calculation allows the identification of said compound. This type of analysis is frequently carried out after carrying out a chemical reaction to verify that the product obtained is as expected.
Note that the sum of percentages equals 100.
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1264
At this point we will determine the formula of a chemical compound from its percentage composition obtained experimentally. Let's see an example:
The percentage composition of methyl succinate is 62.58% C; 9.63% H and 27.79% O. Its molecular mass is 230 amu. Determine the empirical and molecular formula.
- In 100 g of methyl succinate we have: 62.58 g of C; 9.63 g of H and 27.7 g of O
- Conversion of the masses of the elements to moles
$$62.58\;g\;C\cdot\frac{1\;mol\;C}{12.011\;g\;C}=5.210\;mol\;C$$
$$9.63\;g\;H\cdot\frac{1\;mol\;H}{1.008\;g\;H}=9.55\;mol\;H$$
$$27.97\;g\;O\cdot\frac{1\;mol\;O}{15.999\;g\;O}=1.757\;mol\;O$$
Read more: Determination of the empirical and molecular formula
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1200
When burning a substance with the molecular formula of the type C x H y O z , CO 2 and H 2 O are obtained. All the carbon in the sample will go to CO 2 , while the hydrogen will be transformed into H2O, according to the chemical equation:
C x H y O z + O 2 -------> x CO 2 + y/2 H 2 O
The carbon dioxide generated by the combustion is absorbed on sodium hydroxide, determining its mass by difference in weight. While the water vapor is adsorbed on magnesium perchlorate.
Once the masses of CO 2 and H 2 O have been determined, the empirical formula is calculated. Let's see an example:
Read more: Determination of the empirical formula from combustion products
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical compounds
- Hits: 1321
The number or oxidation state indicates the electrons that an atom gains or loses to unite with other atoms and form chemical compounds. Let's apply this concept to the formula unit NaCl. Sodium loses an electron, which chlorine gains, becoming Na + and Cl - . The oxidation state of sodium is +1 and that of chlorine is -1.
In MgCl 2 magnesium loses two electrons to Mg 2+ , these electrons are captured by two chlorine atoms that are transformed into Cl - . Magnesium therefore has oxidation state +2.
To assign the oxidation number we must consider the following rules. In case of contradiction, the rule that goes before in the list prevails.
- The oxidation state of a neutral element or molecule is 0. Cl 2 (EO = 0); H(EO = 0); No 2 (EO = 0)
- The sum of the oxidation states of the atoms that make up a neutral molecule is zero. NaCl (+1-1=0); MgCl 2 (+2-1-1=0)
- Ions have an oxidation number equal to their charge. SO 4 2- (EO = -2); NO 3 - (EO = -1)
- The metals of group 1 (alkali) have an oxidation number of +1 and those of group 2 (alkaline earth) of +2.
- The fluorine atom presents oxidation state -1 in its compounds.
- The oxidation state of hydrogen is +1, except when combined with metals it becomes -1.
- The oxidation state of oxygen in its compounds is -2
- When combined with metals, the oxygen group has EO = -2, the nitrogen group EO = -3, and the halogen group EO = -1