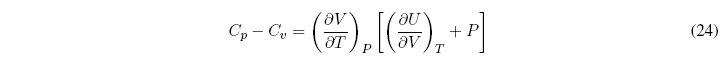The heat capacity of a closed system in an infinitesimal process is defined as the ratio between the heat exchanged and the temperature change produced.
For a process at P=cte, the heat capacity is given by the equation: 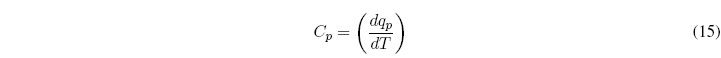
The heat capacity at constant volume is defined in the same way: 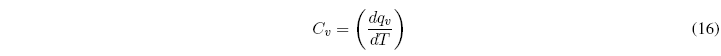
As ![]() , the above equations can be written as:
, the above equations can be written as: 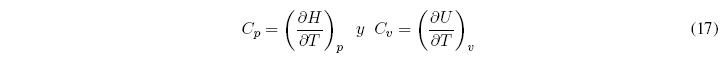
Therefore, C p and C v give us the variation of U and H with respect to temperature and must always take positive values.
We define molar heat capacities for pure substances as the ratio between C p and the number of moles of the substance. 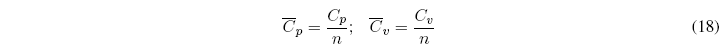
What is the relationship between C p and C v ? 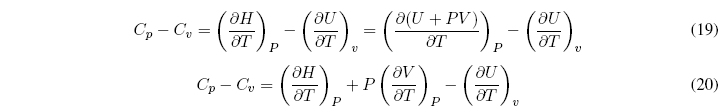
To simplify this equation we consider the internal energy as a function of temperature and volume ![]() , and find the differential
, and find the differential 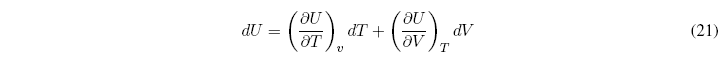
Dividing all terms by dT to P = cte 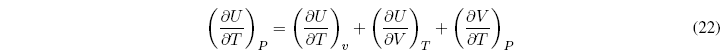
Substituting in the relation C p - C v we get: 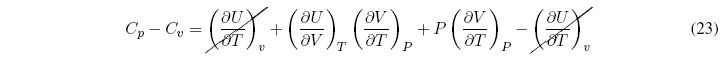
Taking the common factor of the derivative of V with respect to T gives us: