An ideal gas satisfies the equation of state PV = nRT. The interactions between gas molecules are negligible, that is, there are no intermolecular forces. In an ideal gas, the change in volume does not affect the internal energy as long as the temperature is kept constant. A decrease in volume causes the molecules to be closer, but since there are no interactions between them, the internal energy does not change.
An ideal gas is defined as one that satisfies the following equations:
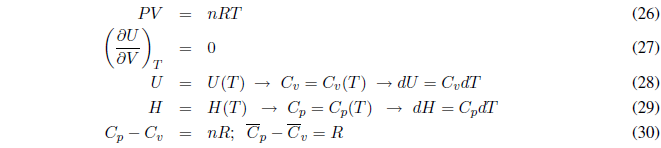
Next we consider some particular processes with ideal gases.