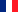
Let the consecutive reactions be $A \stackrel{k_1}{\rightarrow}B\stackrel{k_2}{\rightarrow}C$, of first order, we will determine $[A]$, $[B]$ and $[C]$ as a function of time, assuming $[B]_0 =[C]_0=0$. The variation of $[A]$ in time is given by the expression:
\begin{equation} \frac{d[A]}{dt}=-k_1[A]\label{ec101} \end{equation}
Separating variables and integrating:
\begin{equation} [A]=[A]_0 e^{-k_1 t}\label{ec102} \end{equation}
We now proceed to obtain the variation of $[B] $ with t
\begin{equation} \frac{d[B]}{dt}=k_1[A]-k_2[B] \end{equation}
Substituting $[A]$ for $(\ref{ec102} )$
\begin{equation} \frac{d[B]}{dt}=k_1[A]_0 e^{-k_1 t}-k_2[B] \end{equation}
This differential equation is of the form $\frac{dy}{dx}=f(x)+g(x)y$ and its solution is of the form $y=e^{w(x)}\left[\int e^{-w(x) }f(x)dx+c\right]$, where $w(x)=\int g(x)dx$.
Comparing both equations we arrive at the following equalities: $[B]=y$, $t= x$, $f(x)=k_1 [A]_0 e^{-k1 t}$, $g(x)=-k_2$, $w(x)=\int -k_2 dx=-k_2 x=- k_2 t$.
Therefore, the solution of the differential equation that gives us $[B]$ is:
\begin{equation} [B]=e^{-k_2 t}\left[\int e^{k_2 t}k_1 [A] _0 e^{-k_1 t}dt+c\right] \end{equation}
Integrand:
\begin{equation} [B]=e^{-k_2 t}k_1 [A]_0 \frac{1}{k_2 - k_1}e^{(k_2 - k_1)t}+ce^{-k_2 t} \end{equation}
We calculate the constant of integration, c, with the initial conditions $t=0\;\;\rightarrow [B] =0$ \begin{equation} 0=e^{-k_2 0}\frac{1}{k_2 - k_1}e^{(k_2-k_1)0}+ce^{-k_2 0} \end{equation}
Solving for c:
\begin{equation} c=\frac{-k_1[A]_0}{k_2 - k_1} \end{equation}
Substituting c into the equation for $[B]$
\begin{equation} [B]=\ frac{k_1[A]_0}{k_2-k_1}\left(e^{-k_1 t}-e^{-k_2 t}\right) \end{equation}
Let's get the position of the maximum of [B]:
\begin{equation} \frac{d[B]}{dt}=0=\frac{k_1[A]_0}{k_2-k_1}\left(-k_1e^{-k_1 t}-k_2 e^{- k_2 t}\right) \end{equation}
Simplifying:
\begin{equation} k_1 e^{-k_1 t}=k_2e^{-k_2 t} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \frac{k_2}{ k_1}=e^{(k_2-k_1)t} \end{equation}
Taking neperian logarithm:
\begin{equation} ln\frac{k_2}{k_1}=(k_2-k_1)t \end{equation}
Solving for the maximum time:
\begin{equation} t_m=\frac{ln\frac{k_2}{k_1 }}{k_2-k_1} \end{equation}
Taking this time to [B] we obtain $[B]_m$
\begin{equation} [B]_m=\frac{k_1 [A]_0}{k_2-k_1} \left(e^{-k_1t_m}-e^{-k_2t_m}\right) \end{equation}
The concentration of C as a function of time can be obtained by stoichiometry $[C]=[A]_0 - [A]- [B]$