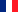
 Molecules that form three covalent bonds, without lone pairs on the central atom, arrange the AB bonds towards the vertices of an equilateral triangle, calling this flat trigonal geometry
Molecules that form three covalent bonds, without lone pairs on the central atom, arrange the AB bonds towards the vertices of an equilateral triangle, calling this flat trigonal geometry
As an example we will analyze the geometry of boron trifluoride, BF 3 . 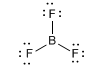
The BF bonds are arranged towards the vertices of an equilateral triangle, with bond angles of 120º.
Chemical bonding II
Planar trigonal molecule, AB3
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: chemical bond II
- Hits: 1370