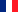
For $n_i$ moles of an electrolyte of the type $M_{\nu_{+}}X_{\nu_{-}}$ we have:
\begin{equation} n_+=\nu_{+}n_i-n_{PI}\ ;\; \Rightarrow\;\;\; dn_+=\nu_{+}dn_i-dn_{PI} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} n_{-}=\nu_{-}n_i-n_{PI}\;\;\;\Rightarrow\; \;\; dn_{-}=\nu_{-}dn_i-dn_{PI} \end{equation}
Writing the Gibbs equation for dG in open systems
\begin{equation} dG=-SdT+VdP+\sum_{i}\mu_{ i}dn_{i}=-SdT+VdP+\mu_Adn_A+\mu_+dn_+ + \mu_-dn_- + \mu_{PI}dn_{PI} \end{equation}
Substituting $dn_-$ and $dn_+$ into this last equation
\begin{equation} dG=-SdT+VdP+\mu_Adn_A+\mu_+\left(\nu_+dn_i-dn_{PI}\right)+\mu_-\left(\mu_-dn_i-dn_{PI} \right)+\mu_{PI}dn_{PI} \end{equation}
The above equation can be simplified if we add electrolyte to the solution keeping temperature, pressure and amount of solvent constant.
\begin{equation} dG=\mu_+\left(\nu_+dn_i-dn_{PI}\right)+\mu_-\left(\mu_-dn_i-dn_{PI}\right)+\mu_{PI} dn_{PI} \end{equation}
Applying the equilibrium condition to the formation of ion pairs
\begin{equation} M^{Z_+}+X^{Z_-}\rightleftharpoons MX^{Z_{+}+Z_- }\;\;\Rightarrow \;\;\;\mu_{PI}=\mu_{+}+\mu_{-} \end{equation}
Substituting this last equation into dG and simplifying
\begin{equation} dG= \mu_+\left( \nu_+dn_i-\cancel{dn_{PI}}\right)+\mu_-\left(\mu_-dn_i-\cancel{dn_{PI}}\right)+(\cancel{ \mu_{+}}+\cancel{\mu_{-}})dn_{PI} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} dG=\nu_+\mu_+dn_i + \nu_- \mu_-dn_i \end{equation}
Therefore,
\begin{equation} \left(\frac{\partial G}{\partial n_i}\right)_{T,P,n_A}=\nu_+\mu_+ + \nu_-\mu_ - \end{equation}
This last equation represents the relationship between the chemical potentials of the salt and that of the ions.
\begin{equation} \mu_i=\nu_+\mu_+ + \nu_-\mu_- \end{equation}
We write the chemical potentials of the positive and negative ions on the molality scale and substitute into the above equation.
\begin{equation} \mu_+=\mu_{+}^{0}+RTln\gamma_{+}\frac{m_+}{m^0}\;\;\;\;\;\;\mu_ {-}=\mu_{-}^{0}+RTln\gamma_{-}\frac{m_-}{m^0} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \mu_i=\nu_+\left( \mu_{+}^{0}+RTln\gamma_{+}\frac{m_+}{m^0}\right)+\nu_-\left(\mu_{-}^{0}+RTln\gamma_ {-}\frac{m_-}{m^0}\right) \end{equation}
Grouping terms
\begin{equation} \mu_i=\nu_+\mu_{+}^{0}+\nu_{-} \mu_{-}^{0}\left[\gamma_{+}^{\nu_+}\gamma_{-}^{\nu_-}\left(\frac{m_+}{m^0}\right )^{\nu_+}\left(\frac{m_-}{m^0}\right)^{\nu_-}\right] \end{equation}
Calling $\mu_{i}^{0}= \nu_+\mu_{+}^{0}+\nu_-\mu_{-}^{0};\;\;\;\gamma_{\pm}^{\nu}=\gamma_{+}^ {\nu_+}\gamma_{-}^{\nu_-}\;\;\;\nu=\nu_++\nu_-$. Therefore,
\begin{equation} \mu_i=\mu_{i}^{0}+RTln\left[\gamma_{\pm}^{\nu}\left(\frac{m_+}{m^0} \right)^{\nu_+}\left(\frac{m_-}{m^{0}}\right)^{\nu_-}\right] \end{equation}