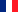
For a reversible reaction $A\rightleftharpoons C$ of the first order, with kinetic constants for the forward reaction $k_1$ and reverse reaction $k{-1}$, we will determine $[A]$ and $[C]$ as a function of time , assuming that $[C]_0=0$. The variation of $[A]$ in time is given by the expression: \begin{equation}\label{1} \frac{d[A]}{dt}=-k_1[A]+k_{-1 }[C] \end{equation} From the stoichiometry we deduce, $[C]=[A]_0 -[A]$, substituting in $(\ref{1})$ \begin{equation} \frac{d[ A]}{dt}=-k_1[A]+k_{-1}\left([A]_0 - [A]\right) \end{equation}
Separating variables and integrating: \begin{equation} \int_{ [A]_0}^{[A]}\frac{d[A]}{k_{-1}[A]_0 -\left(k_1+k_{-1}\right)[A]}=\int_ {0}^{t}dt \end{equation} The integral is immediate natural type if we multiply and divide by the derivative of the denominator. \begin{equation} \frac{1}{-(k_1 +k_{-1})}ln\frac{k_{-1}[A]_0-(k_1 +k_{-1})[A]}{ \cancel{k_{-1}[A]_0}-(k_1 +\cancel{k_{-1}})[A]_0}=t \end{equation} We can only solve $[A]$ from this last equation: \begin{equation} ln\frac{k{-1}[A]_0 -(k_1 +k_{-1})[A]}{-k_1[A]_0}=-(k_1+k_{ -1})t \end{equation} \begin{equation} k_{-1}[A]_0-(k_1+k_{-1})[A]=-k_1[A]_0 e^{-(k_1 +k_{-1})t} \end{equation} \begin{equation} (k_1+k_{-1})[A]=[A]_0\left[k_{-1}+k_1 e^{- (k_1+k_{-1})t}\right] \end{equation} \begin{equation} [A]=\frac{[A]_0}{k_1+k_{-1}}\left[k_{ -1}+k_1 e^{-(k_1+k_{-1})t}\right] \end{equation} The calculation of $[C]$ can be done using the relation $[C]=[A]_0 -[A]$ \begin{equation} [C]=[A]_0\left[1-\frac{1}{k_1+k_{-1}}\left(k_1+k_1 e^{-(k_1+ k_{-1})t}\right)\right] \end{equation} Once equilibrium $t\rightarrow \infty$ has been reached, the concentrations of reactant and product will be given by: \begin{equation} [A]_ {e}=\frac{[A]_0k_{-1}}{k_1+k_{-1}} \end{equation} \begin{equation} [C]_{e}=\frac{[A]_0 k_1}{k_1+k_{-1}} \end{equation} The quotient between both equilibrium concentrations gives us a relationship between the kinetic constant of the forward and reverse reaction. \begin{equation} \frac{[C]_{e}}{[A]_{e}}=\frac{k_1}{k_{-1}}\;\; \rightarrow [C]_{e}=\frac{k_1}{k_{-1}}[A]_{e} \end{equation}