A heat engine is a cyclically operating device that absorbs a quantity of heat from a hot source (for example, the boiler), does work -w on the surroundings, and releases a quantity of heat to a cold source.

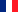
The output or efficiency of a heat engine is the fraction of energy supplied that is converted into work. The machine consumes energy \(q_c\) per cycle and does work \(-w\), so the yield will be:
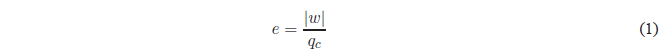
We are going to express the performance as a function of the temperatures of the hot and cold bulb.
As can be seen in the schematic of the heat engine,
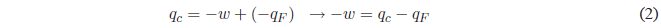
Substituting w into the yield gives us:
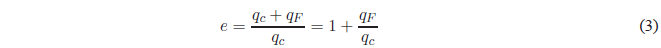
Since \(q_F\) is negative and \(q_c\) is positive the return is always less than 1.