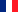
Consider a moving particle of mass m, whose position vector is $\vec{r}=x\vec{i}+y\vec{j}+z\vec{k}$. Let the linear momentum of the particle be $\vec{p}=p_{x}\vec{i}+p_{y}\vec{j}+p_{z}\vec{k}$
The angular momentum of the particle, $\vec{l}$ is defined: \begin{equation} \vec{l}=\vec{r}\times\vec{p}=\left(yp_{z}-zp_ {y}\right)\vec{i}-\left(xp_{z}-zp_{x}\right)\vec{j}+\left(xp_{y}-yp_{x}\right)\vec {k} \end{equation} \begin{eqnarray} l_{x} &=& yp_z - zp_y\\ l_{y} &=& zp_x - zp_z\\ l_{z} &=& xp_y - yp_x \end{eqnarray}